一、图模型——Labeled Property Graph Model
- A labeled property graph is made up of nodes, relationships, properties, and labels.
- Nodes contain properties. Think of nodes as documents that store properties in the form of arbitrary key-value pairs. In Neo4j, the keys are strings and the values are the Java string and primitive data types, plus arrays of these types.
- Nodes can be tagged with one or more labels. Labels group nodes together, and indicate the roles they play within the dataset.
- Relationships connect nodes and structure the graph. A relationship always has a direction, a single name, and a start node and an end node—there are no dangling relationships. Together, a relationship’s direction and name add semantic clarity to the structuring of nodes.
-
Like nodes, relationships can also have properties. The ability to add properties to relationships is particularly useful for providing additional metadata for graph algorithms, adding additional semantics to relationships (including quality and weight), and for constraining queries at runtime.
- Nodes
- Are often used to represent entities
- Can be tagged with one or more labels
- Can contain properties
- Relationships:
- Connect nodes and structure the graph
- Directed
- Always have a single name, a start node and an end node ⇒ no dangling relationships
- Can have properties
- Properties:key-value pairs (named values):
- Key is the name of the property, and Always a string
- Values can be:
- Numeric values
- String values
- Boolean values
- Lists of any other type of value
- Labels: Group nodes together
- Used to assign types to nodes
- Groups nodes into sets: all nodes with the same label belong to the same set
- Database queries can be constrained to these sets instead of the whole graph more efficient queries that are easier to write
- Each node can has any number of labels (including none)
具体来说,neo4j的数据结构和类型如下:
- Nodes
- Id
- Label(s)
- Map (of properties)
- Relationships
- Id
- Type
- Map (of properties)
- Id of the start and end nodes
- Paths
- An alternating sequence of nodes and relationships
其中Property的key是String类型,value只能是如下几种类型:
- Property types
- Number
- Integer
- Float
- String
- Boolean
- and array of the above types(以及上面这些类型的数组形式)
- Number
NOTES neo4j的property不能是嵌套类型(map)。
二、查询语言——Cypher
Cypher is an expressive (yet compact) graph database query language.
TIPS 其他的图查询语言
- SPARQL: 主要针对RDF图模型
- Gremlin: 类似于DSL
- AQL: ArangoDB的查询语言
底层API :TODO
三、图遍历——index-free adjacency
index-free adjacency
- Each node “knows” (i.e. directly points to) its adjacent nodes - index-free adjacency
- No explicit index → each node acts as micro-index of nearby nodes → much cheaper than global indices
- Because of this, query times are less/not dependent of the size of the graph → they depend only on the part of the graph that has been searched
- Precomputes and stores bidirectional joins as relationships (i.e. no need to compute them)
- Enables bidirectional traversal of the database: we can traverse both incoming and outgoing relationships
另一种方式是index-based adjacency,对应的开源图数据库有ArangoDB。关于两者的优劣有一个讨论:Index Free Adjacency or Hybrid Indexes for Graph Databases。
个人认为如果分布式环境下,index-free adjacency要保证邻近节点能够尽量保存在同台机器,减少网络的交互才有意义(事实上,neo4j就是单机的全量数据,所有数据都在一台机器上,集群中的数据都是对等的,不是sharding。)。另外,index-free adjacency的拥护者在对比性能的时候一直说index-based adjacency需要O(log n),而它们只需要O(1),而实际上如果采用Hash索引,完全是可以达到O(1)性能的。事实上,ArangoDB在所有的性能测试中都是靠前的。
四、图存储
- there are separate stores for nodes, relationships, labels, and properties(这点很特别,属性不是随着节点存储的)
- It all boils down to linked list of fixed size record on disk。基本都是定长记录(fixed-size record store),方便根据id简单快速计算出偏移量定位到记录。
- Properties are stored as linked list of property records, each holding key+value. (这点很特别,属性不是随着节点存储的,这是为了让节点尽量简单而且定长。)
- Each node/relationship references its first property record. (真的是linkes list)
- The Nodes also reference the first relationship in its relationship chain. (节点包含关系链的第一个关系的引用)
- Each Relationship references its start and end node. (每个关系包括起始节点的引用)
- it also references the prev/next relationship record for the start/end node respectively. (同一个起/始节点的关系也是以double linked list的方式串联起来。形成双向关系链表。)
TIPS index-free adjacency的关键
fixed-sized records + pointer-like record IDs = index-free adjacency
将动态的关系分开存储,节点和关系只存储图结构,从而保证定长。这个是所谓的index-free adjacency的实现关键,在node节点中存放关系id,通过O(1)定位到关系记录而不是通常的O(log n)。
具体存储格式如下图所示:
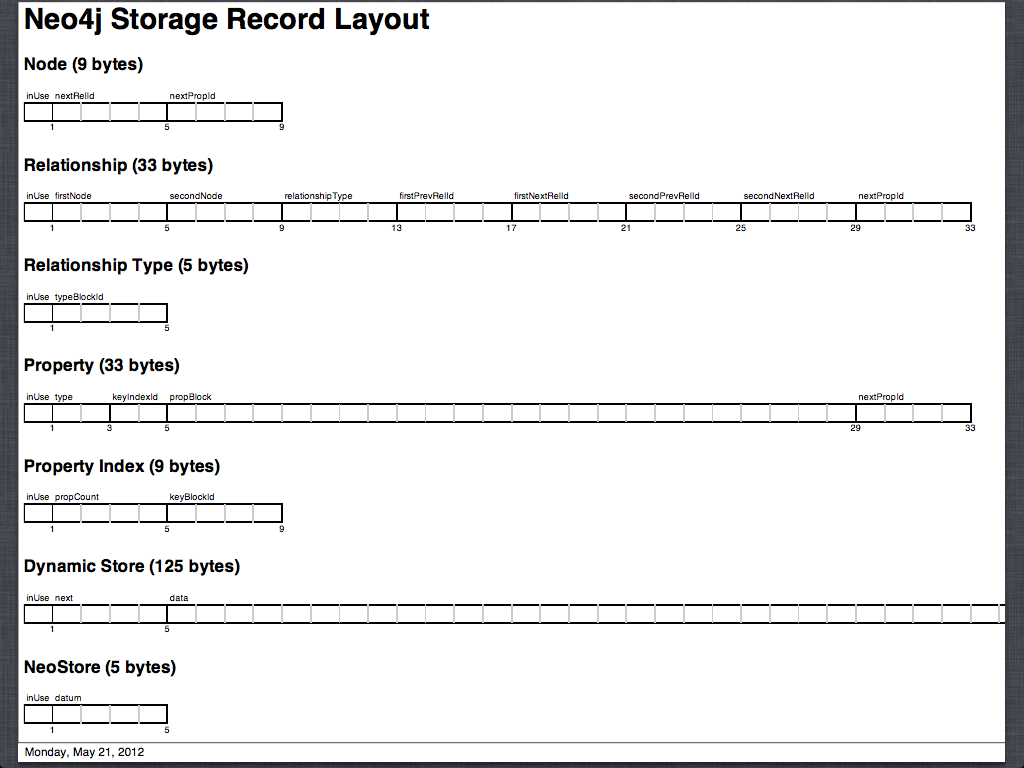
nodes
- Node store: neostore.nodestore.db
- fixed-sized records: 15 bytes
- inUser:1 (1 byte)
- nextRelId: 2~5 (4 bytes):第一个关系的指针
- nextPropId: 6~9 (4 bytes): 第一个属性的指针
- labels: 10~14 (5 bytes):The five bytes for labels point to the label store for this node
- extra: 15 (1 byte)
relationships
- Relationship store: neostore.relationshipstore.db; 34 bytes
- inUser:1 (1 byte)
- firstNode: 2~5 (4 bytes): from节点id
- secondNode: 6~9 (4 bytes): to节点id
- relationshipType: 10~13 (4 bytes): a pointer to the relationship type (which is stored in the relationship type store)
- firstPrevRelId: 14~17 (4 bytes): from节点的上一个关系
- firstNextRelId: 18~21 (4 bytes): from节点的下一个关系
- secondPrevRelId: 22~25 (4 bytes): to节点的上一个关系
- secondNextRelId: 26~29 (4 bytes): to节点的下一个关系
- nextPropId: 30~33 (4 bytes): 第一个属性的指针
- firstInChainMarker: 34 (1 byte): a flag indicating whether the current record is the first in what’s often called the relationship chain.
- Relationship type store: neostore.relationshiptypestore.db; 5 bytes
- inUser:1 (1 byte)
- typeBlockId: 2~5 (4 bytes)
TIPS 关系存储中的双向链表
neo4j的关系记录中以双向链表的形式存储了from节点和to节点的整个关系链,方便对关系关联的节点进行关系遍历,这也是为什么节点记录只存储了起始节点指针的原因。
properties
- Property store: neostore.propertys tore.db; 24 bytes
- inUser:1 (1 byte)
- unuserd: 2 (1 byte)
- The 4 high bits of next pointer:3 (1 byte)
- type: 3~4 (2 bytes): the type of the propety, int, String, long, etc.
- keyIndexId: 4~5 (2 bytes): id of the property index
- prevPropId: 14~17 (4 bytes): ID of the previous property in the property chain
- nextPropId: 14~17 (4 bytes): ID of the next property in the property chain
- data: 18~24 (8 bytes): a long that is an id to a DynamicStore (a DynamicStringStore or DynamicArrayStore, depending on they property Type, stored either in “neostore.propertystore.db.strings” or “neostore.propertystore.db.arrays”) that stores the value OR (depending on the Type field) the actual value (there is no need to redirect to another file if the Type is integer and can be held there)。
- Property key store: neostore.propertystore.db.index.keys; 9 bytes
- inUser:1 (1 byte)
- propCount: 2~5 (4 bytes)
- keyBlockId: 6~9 (4 bytes)
- Property (long) string store: neostore.propertystore.db.strings:存储 property (key-value 结构)的Value值是字符串的数据。
- Property array store: neostore.propertystore.db.arrays:存储 property (key-value 结构)的Value值是数组的数据
其他的存储还有label存储、schema存储、版本信息存储、活跃日志存储等,这些相对不是很重要,这里就不展开了。
NOTES
Property的data部分采用了定长的8字节存储数据本身或者ID到变长数据(long string或者array)。但是对于int类型的数据8个字节有点浪费。所以新版的neo4j做了优化。具体参见 Neo4j High Performance (2015)。总之,Property也是定长的。
五、图索引
- 入口节点/边索引:集成Lucene用于倒排检索,支持精确、模糊、范围和地理位置查询
- 图遍历索引:依赖于index-free adjacency进行快速的迭代(iterating)和条件过滤(filtering)
With a graph database, most queries follow a pattern whereby an index is used simply to find a starting node (or nodes). The remainder of the traversal then uses a combination of pointer chasing and pattern matching to search the data store.
TIPS
- lecene等倒排索引虽然可以支持精确、模糊、范围和地理位置多种条件查询,但是性能上并不是最优
- 很多开源图存储,如Titan、ArangoDB等会引入Vertex-Centric Indexes解决图遍历过程中的supernode问题
六、缓存
- four different types of caches:
- NoCache: This is degenerate and stores nothing
- LruCache: This utilizes LinkedHashMap of the java.util package along with a custom method to remove the oldest entry when deallocating space—removeEldestEntry(); this makes it an adaptable LRU cache
- SoftLruCache: An LruCache using soft values to store references and queues for garbage-collected reference instances
- WeakLruCache: An LruCache using hard values to store references and queues for garbage-collected reference instances
- LRU-K page cache for nodes and relationships
- makes extensive use of the java.nio package(大量使用堆外内存)
- makes use of the SoftReference and WeakReference objects
七、事务
- Write-Ahead Log (WAL): ensures atomicity and durability in transactions, also used for failure recovery.
- LogEntry: Commands + information for phases
- Changes made in the transaction are collected as commands, 可幂操作
- Recovery simply replays all transactions since the last safe point
- LogEntry State:
- Start: This indicates that the transaction is now active
- Prepare: This indicates that the transaction is being prepped for a commit
- OnePhaseCommit: This initiates a commit in EmbeddedGraphDatabase
- TwoPhaseCommit: This initiates commits in a distributed scenario
- Done: This indicates that a transaction is complete
- Command (not an actual state): Encapsulation for the commands in the transaction
- Locking
- RWLock(Read Write Lock): ReentrantReadWriteLock
- LockManager: synchronization of RWLock accesses, or creation of the locks and, whenever required, passing an instance of the RAGManager and appropriate removal at times.
- RAGManager(Resource Allocation Graph Manager): detect whether waiting on a resource can lead to possible future deadlocks
- Wait-For Graph (WFG): stores a graph of the resources and threads waiting on a RWLock.
八、高可用(HA)
- master-slave cluster with master election
- atomic broadcast
- used to send messages to all instances in a reliable manner
- no loss of message
- preserved message ordering
- no messages are corrupt or duplicated
- Apache Zookeeper is used to implement the Atomic Broadcast protocol (around Version 1.8)
- used to send messages to all instances in a reliable manner
- Replication but not sharding!
- replication out from master to slaves at frequent intervals
- All transaction are committed through the master
- Then (eventually) applied to the slaves
- Eventuality defined by the update interval or when synchronization is mandated by interaction
- write-master with read-slaves but also supports writing through slaves
- When writing to a slave:
- Locks coordinated through the master
- Thansaction data buffered on the slave, applied first on the master to get a txid, then applied with the same txid on the slave
九、Scale
因为不支持sharding,所以其实图的大小和吞吐率(主要是写)是比较受限的。当然,引入sharding,对图分割的合理性是一个挑战,处理不好很容易引起剧烈的性能下降。 当然,对于neo4j,之所以不支持sharding,我觉得客观原因有如下两个:
- 因为它的index-free adjacency实现依赖于存储指针(ID),而这个指针能够快速转换成偏移量很大程度上依赖于本地定长记录,可以很方便快速的计算出记录的偏移量
- 入口节点/边的索引依赖于lucene,而分布式索引(类似于ES)的构建并不是一个简单的问题
不过即使不sharding,neo4j单机的性能还是可以的:
1、Capacity (graph size)
can support single graphs having tens of billions of nodes, relationships, and properties.
2、Latency (response time)
With a graph database, most queries follow a pattern whereby an index is used simply to find a starting node (or nodes). The remainder of the traversal then uses a combination of pointer chasing and pattern matching to search the data store.
3、Read and write throughput
neo4j启动
[arganzheng@st01-bda-asp01 neo4j-community-3.3.0]$ bin/neo4j
Usage: neo4j { console | start | stop | restart | status | version }
[arganzheng@st01-bda-asp01 neo4j-community-3.3.0]$ bin/neo4j start
Active database: graph.db
Directories in use:
home: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0
config: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/conf
logs: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/logs
plugins: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/plugins
import: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/import
data: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/data
certificates: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/certificates
run: /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/run
Starting Neo4j.
Started neo4j (pid 37024). It is available at http://0.0.0.0:8474/
There may be a short delay until the server is ready.
See /home/arganzheng/neo4j-community-3.3.0/logs/neo4j.log for current status.
neo4j 调优
mac下JVM参数设置,在/Applications/Neo4j Community Edition 3.2.6.app/Contents/Resources/app/bin/neo4j-community.vmoptions`文件:
# Enter one VM parameter per line, note that some parameters can only be set once.
# For example, to adjust the maximum memory usage to 512 MB, uncomment the following line
-Xmx2g -Xms2g
-include-options ${installer:userVmOptionsFile}
Neo4j的不足
1、neo4j没有namespace的概念 2、不支持动态label和动态关系类型,这个限制非常蛋疼,对于需要根据label或者type进行查询的语句只能进行服务端字符串拼接。 3、不支持嵌套属性和嵌套索引 4、全文索引不支持schema indexes,只能通过legacy indexing实现(全文检索还可以通过auto indexes实现) 5、关系索引不支持schema indexes,只能通过legacy manual indexes实现(Relationship indexes),这意味着只能使用embedded模式访问neo4j。这也意味着neo4j没办法解决supernode问题。 6、社区版不支持在线备份(online backup)、HA & Scalability(集群)和监控 7、企业版的老的集群方案是基于replication的Master-Slave架构,这意味着master具有写入单点问题,并且写不具有可扩展性。新的集群方案引入了Core Servers角色,各个core servers之间通过Raft协议进行数据同步和集群管理。但是这个只是解决了写入的单点问题,并没有解决写入的可扩展性问题(每个core server的写入操作并没有因为server的增加而减少),相反,对应用来说写入的时间还变长了(需要等待 N/2+1 的 core servers返回) 8、两种集群方案都是全量的单机数据,不是sharding架构。因此图的数据规模和单次图计算能力还是取决于单机。 9、偏向于OLTP,OLAP基本没有支持。
参考文章
- Neo4j索引笔记之SchemaIndex和LegacyIndex
- Welcome to the Dark Side: Neo4j Worst Practices (& How to Avoid Them)
- An overview of Neo4j Internals 非常不错的PPT!
- How is Neo4j stored on a disk? Is it some kind of adjacent matrix stored in a relational database?