问题1 如何让web容器加载你的web MVC框架
对于基于servlet的web容器来说,遵循的是servlet规范,入口配置文件是web.xml。这类web容器会在启动的时候会而且仅会加载如下三种类型的对象:
- servlet
- context listener
- filter
而且有一定的加载和销毁顺序!
Loading Servlets, Context Listeners, and Filters
Servlets, Context Listeners, and Filters are loaded and destroyed in the following order:
Order of loading:
- Context Listeners
- Filters
- Servlets
Order of destruction:
- Servlets
- Filters
- Context Listeners
Servlets and filters are loaded in the same order they are defined in the web.xml file and unloaded in reverse order. Context listeners are loaded in the following order:
- All context listeners in the web.xml file in the order as specified in the file
- Packaged JAR files containing tag library descriptors
- Tag library descriptors in the WEB-INF directory
一般来说servlet用于接收用户请求,filter作为servlet的拦截器,context listener则作为事件监听器。所以一般都是使用servlet来加载web MVC框架。
对于Spring MVC来说,官方文档有很详细的描述:15. Web MVC framework
spring MVC是通过DispatcherServlet这个Front Controller启动的。而DispatcherServlet本身就是一个servlet,配置在web.xml中:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>foobar</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>foobar</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
问题2:你的web MVC框架又是怎么加载你的web-aware Spring ApplicationContext?
前面简单配置我们已经让web容器加载我们的web MVC框架启动类DispatcherServlet了,那么DispatcherServlet又是怎么加载我们的应用上下文呢?
在Spring MVC官方文档 15. Web MVC framework 中有这么一句话:
As detailed in Section 3.13, “Additional Capabilities of the ApplicationContext”, ApplicationContext instances in Spring can be scoped. In the Web MVC framework, each DispatcherServlet has its own WebApplicationContext, which inherits all the beans already defined in the root WebApplicationContext. These inherited beans can be overridden in the servlet-specific scope, and you can define new scope-specific beans local to a given servlet instance.
正如web容器的入口配置文件是web.xml一样,每个web MVC框架也都有自己的配置文件,对于SpringMVC来说,其配置文件默认为WEB-INF/${dispatcherServletName}-servlet.xml。对于上面的例子,DispatchServlet载入后,它将从foobar-servlet.xml中加载应用上下文。
分解应用上下文
根据前面的配置,DispatcherServlet已经载入foobar-servlet.xml。你可以将系统中所有的bean都配置在foobar-servlet.xml中,但是最后这个文件会非常臃肿,最佳实践是对每一层(web、biz、dal)进行单独配置,至少要区分web层配置和biz层的配置。
为了保证所有的配置文件都可以被载入,我们需要在web.xml文件中配置一个上下文载入器。
Configuring a context loader
To ensure that all of these configuration files are loaded, you’ll need to configure a context loader in your web.xml file. A context loader loads context configura- tion files in addition to the one that DispatcherServlet loads. The most com- monly used context loader is a servlet listener called ContextLoaderListener that is configured in web.xml as follows:
<listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
NOTE Some web containers do not initialize servlet listeners before servlets— which is important when loading Spring context definitions. If your application is going to be deployed to an older web container that adheres to Servlet 2.2 or if the web container is a Servlet 2.3 container that does not initialize listeners before servlets, you’ll want to use ContextLoaderServlet instead of ContextLoaderListener.
配置好ContextLoaderListener之后,我们需要告诉它哪些文件需要它加载,否者默认它会加载/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,这是通过设置contextConfigLocation parameter in the servlet context:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/foobar-service.xml
/WEB-INF/foobar-data.xml
/WEB-INF/foobar-security.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
为什么不使用Spring的import标签引入多个文件 How To Load Multiple Spring Bean Configuration File
File : Spring-All-Module.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <import resource="common/Spring-Common.xml"/> <import resource="connection/Spring-Connection.xml"/> <import resource="moduleA/Spring-ModuleA.xml"/>
</beans>
这是因为使用ContextLoaderListener载入的应用上下文会作为DispatcherServlet载入的应用上下文(the WebApplicationContext for this servlet)的根应用上下文(root application context)被所有的DispatherServlet载入上下文共享。
A web application can define any number of DispatcherServlets. Each servlet will operate in its own namespace, loading its own application context with mappings, handlers, etc. Only the root application context as loaded by ` org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener`, if any, will be shared.
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
...
}
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean {
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
…
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
…
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext wac = findWebApplicationContext();
if (wac == null) {
// No fixed context defined for this servlet - create a local one.
WebApplicationContext parent = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
wac = createWebApplicationContext(parent);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Apparently not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh support:
// triggering initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
}
其中WebApplicationContext parent = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
ContextLoaderListener加载的根应用上下文:
WebApplicationContext org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc)
Find the root WebApplicationContext for this web application, which is typically loaded via org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.
其实它仅仅是查找ServletContext中有没有key为WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE的值:
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
return getWebApplicationContext(sc, WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, String attrName) {
Assert.notNull(sc, "ServletContext must not be null");
Object attr = sc.getAttribute(attrName);
if (attr == null) {
return null;
}
if (attr instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Exception) {
throw new IllegalStateException((Exception) attr);
}
if (!(attr instanceof WebApplicationContext)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Context attribute is not of type WebApplicationContext: " + attr);
}
return (WebApplicationContext) attr;
}
因为ContextLoaderListener加载完后以这个key将它放在了ServletContext中。
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
}
public class ContextLoader {
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
…
try {
// Determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
...
return this.context;
}
...
}
}
Spring官方文档给出了这么一个图:
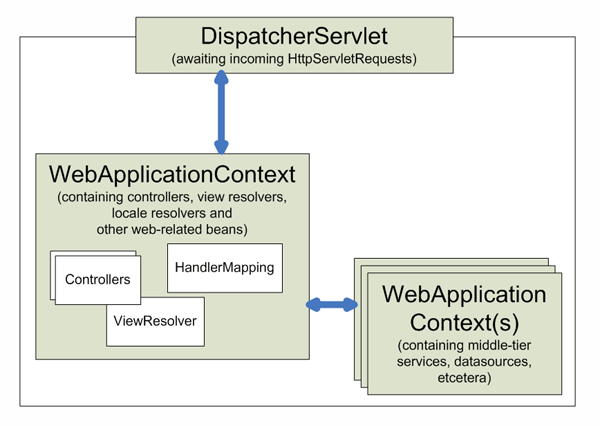
然而这个图是不正确的!在这个图里,DispatcherServlet加载的WebApplicationContext跟biz层的WebApplicationContext(s)(即root ApplicationContext,这个称谓本身就有点怪,有误导嫌疑!),是一对多的关系!其实应该反过来。从上面的代码看来,通过WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext)拿到的rootApplicationContext,是所有DispatcherServlet共享的biz层的应用上下文(这点从传递servletContext参数也可以看出来,因为ServletContext本身就是application级别的),它是作为每个DispatcherServlet加载的web ApplicationContext容器的parent上下文,进行共享。
这点可以很简单的通过如下方式进行验证:在web层用WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext看能不能拿到DispatcherServlet所载入的web ApplicationContext。笔者试验了一下,确实拿不到,因为root ApplicationContext(parent)感知不到也不care,每个DispatcherServlet载入的webApplication(children)。
–EOF–